About growing low pollen forests
Growing low pollen forests
Replacing with low-pollen cedars and cypresses.
Many people suffer from hay fever every year.
The Tokyo Metropolitan Government has been working on measures to combat hay fever since 1983, but now it is estimated that 48.8% of The Tokyo citizens are hay fever.
Tokyo is famed for its globally large city, but about 40% of the total area is forest, and about 70% of it is located in the mountainous area of Tama. The wide-ranging artificial forests of more than 30-year-old cedars and cypresses are producing a lot of pollen.
The Tokyo Development Foundation for Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries has been working together with the Tokyo Metropolitan Government to "grow low pollen forests" since 2006 by cutting down artificial cedar and cypress forests that scatter a lot of pollen, and replacing them with low-pollen cedars (*). Not only are we reducing the amount of pollen that is the cause of hay fever, we are stimulating the circulation of forests aiming at the stable supply of lumber and the activation of forestry as well.
(*) Low-pollen cedars have about 1/100 the amount of pollen compared to regular cedars.
There are three varieties being developed in Tokyo.
We will afforest mountains with low-pollen saplings such as cedars.
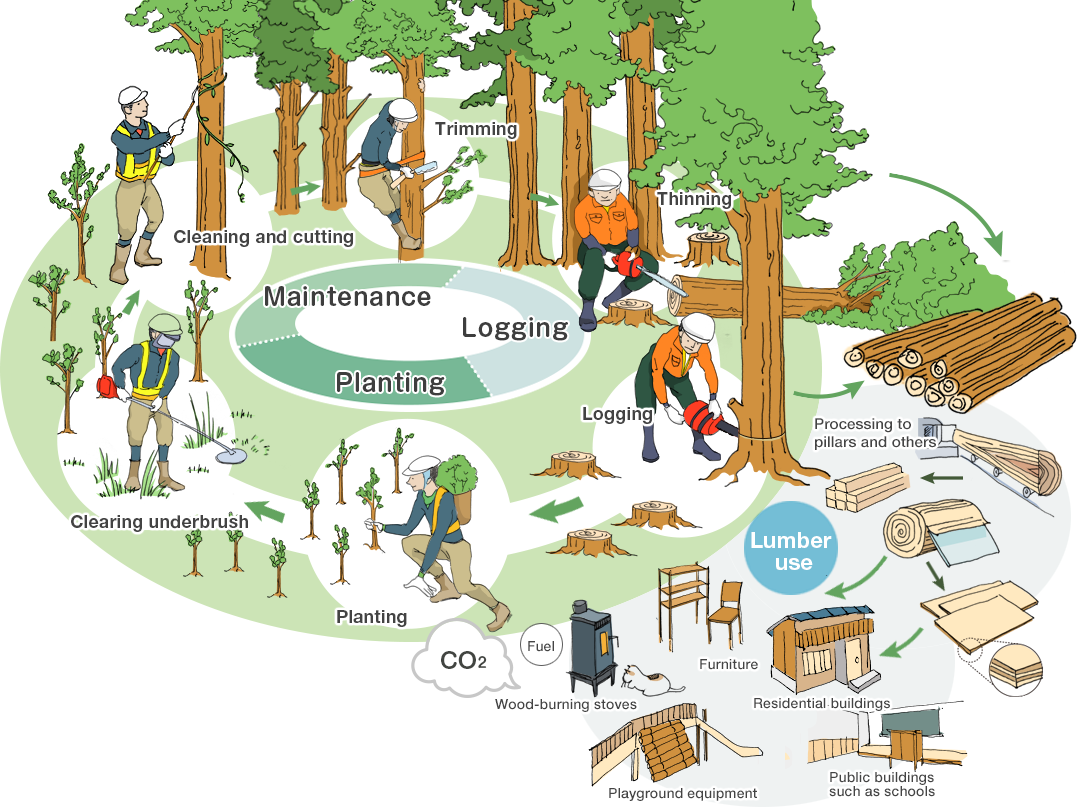
Circulation of forests
Utilize logged trees, and afforest after the logging Repeat
Artificial forests are created with trees planted by humans. Without proper care, they will become over crowded, and the trees will not fully grow. Also, the crowded trees prevent the sunlight reaching the ground. Without sufficient light, grass won’t grow. As a result, landslides and floods are likely to occur due to the poor soil conditions.
Forest care is inevitable in order to maintain healthy forests where big trees can grow and plenty of water can be stored. It is very important to "circulate forests" by cutting down grown trees to utilize and performing afforestation afterwards.
-
Planting
Plant saplings of "low-pollen cedars and cypresses" on the land after logging.
-
Clearing underbrush
Cut weeds growing around the saplings.
-
Cleaning and cutting
Remove vines and bent trees for growing trees.
-
Trimming
Remove undesirable branches to maintain quality wood.
-
Thinning
Thin out trees so that sunlight reaches into the forest.
-
Logging
Cut down fully grown trees.
-
Lumber use
Process the logs cut out of the forest into boards, squared timbers or plywood, and use them for residential buildings and furniture.
Join in the growing of forests
Growing healthy forests together and making them sustainable in the future
Growing a forest from planting saplings takes much time and effort.
There are several ways to participate in growing low pollen forests, such as making a donation to the fund raising, participating in forest volunteer activities, and choosing lumber from Tama, Tokyo's wood.
In the campaign for growing low pollen forests, we are welcoming many participants to take control of healthy forests in the future while contributing to the prevention of global warming.